Modular Photoredox System with Extreme Reduction Potentials Based on Pyridine Catalysis.
Abstract
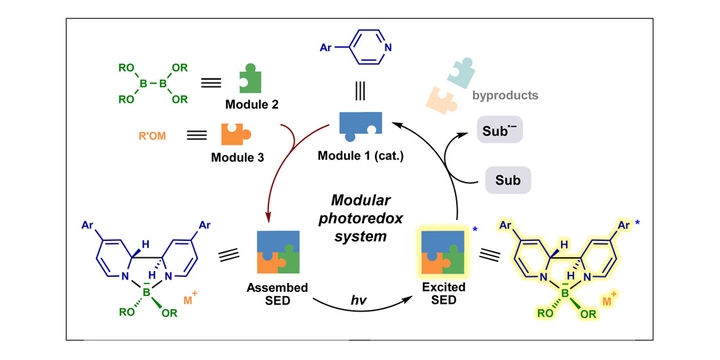
Photoinduced electron transfer is an efficient approach to single-electron reduction of organic molecules for their activation. A variety of molecular photoredox systems have been developed for this purpose, whereas only a few of them exhibit potent reduction abilities required for reducing inert substrates, and more new systems with extreme reduction potentials are highly desirable. Notably, developing a new photoredox system usually requires iterative work on molecular design and synthesis. In this work, we present a conceptually distinct modular photoredox system, which features the in situ formation of a photoredox-active species from three simple modules (a pyridine derivative as catalyst, and a diboron[4] compound and an alcoholate as sacrificial components). This allowed for flexible tuning of its property to approach extreme reduction potentials, enabling a wide range of challenging single-electron reduction reactions. This work extends the utility of pyridine catalysis and serves as the proof of concept of the molecular photoredox system.