Pd(II)-Catalyzed Regioselective 2-Alkylation of Indoles via a Norbornene-Mediated C–H Activation: Mechanism and Applications.
Abstract
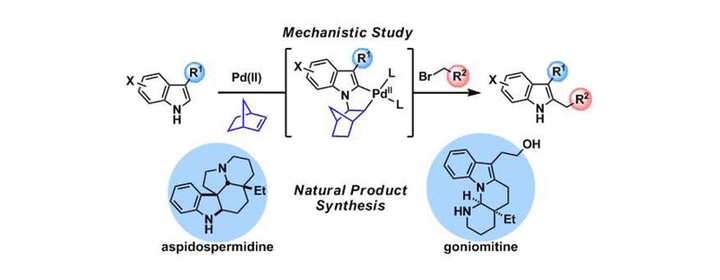
A palladium-catalyzed direct 2-alkylation reaction of free N-H indoles was developed based on a norbornene-mediated regioselective cascade C–H activation. The detailed reaction mechanism was investigated by NMR spectroscopic analyses, characterization of the key intermediate, deuterium labeling experiments, and kinetic studies. The results indicate that a catalytic cycle operates, in which an N-norbornene type palladacycle is formed as the key intermediate. Oxidative addition of alkyl bromide to the Pd(II) center in this intermediate is the rate-determining step of the reaction. The synthetic utility of this indole 2-alkylation method was demonstrated by its application in natural product total synthesis. A new and general strategy to synthesize Aspidosperma alkaloids was established employing the indole 2-alkylation reaction as the key step, and two structurally different Aspidosperma alkaloids, aspidospermidine and goniomitine, were synthesized in concise routes.